1. The Ribbon
- The new tabbed Ribbon system was introduced in Word 2007 to replace traditional menus.
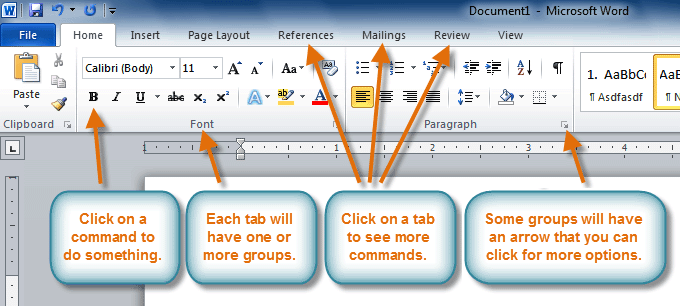
- The Ribbon contains all of the commands you'll need in order to perform common tasks. It contains multiple tabs, each with several groups of commands, and you can add your own tabs that contain your favorite commands.
- Some groups have an arrow in the bottom-right corner that you can click to see even more commands.
- Certain programs, such as Adobe Acrobat Reader, may install additional tabs to the Ribbon. These tabs are called add-ins.
I. How To minimize and maximize the Ribbon:
The Ribbon is designed to be easy to use and responsive to your current task; however, you can choose to minimize it if it's taking up too much screen space.
- Click the arrow in the upper-right corner of the Ribbon to minimize it.
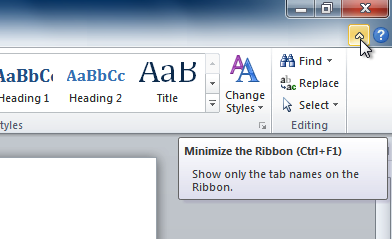
- To maximize the Ribbon, click the arrow again.
When the Ribbon is minimized, you can make it reappear by clicking on a tab. However, the Ribbon will disappear again when you are not using it.
II. How To customize the Ribbon:
You can customize the Ribbon by creating your own tabs with the commands you want.
- Right-click the Ribbon and select Customize the Ribbon. A dialog box will appear.
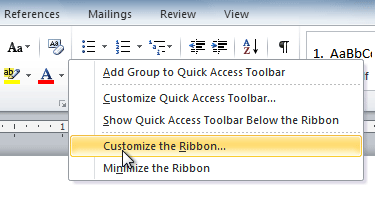
- Click New Tab. A new tab will be created with a new group inside it.
- Make sure the new group is selected.
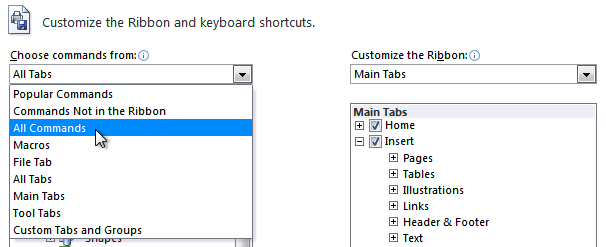
- Select a command from the list on the left, then click Add. You can also drag commands directly into a group.
- When you are done adding commands, click OK.
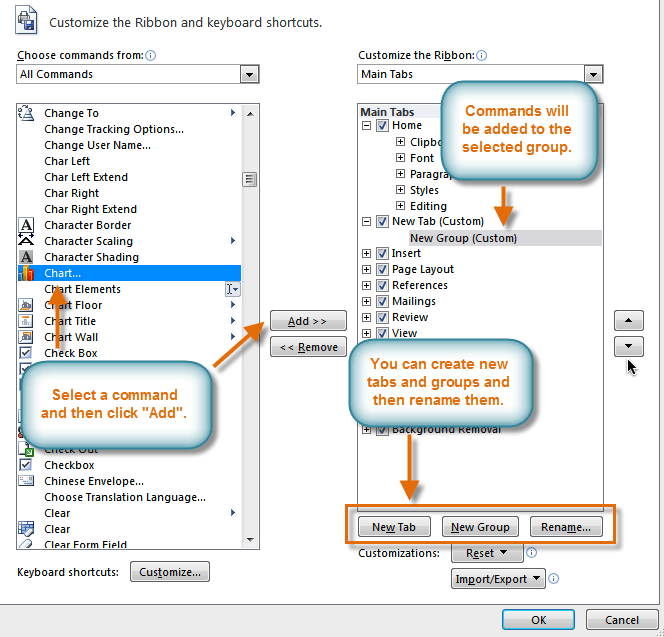
If you don't see the command you want, click the Choose commands from: drop-down box, then select All Commands.
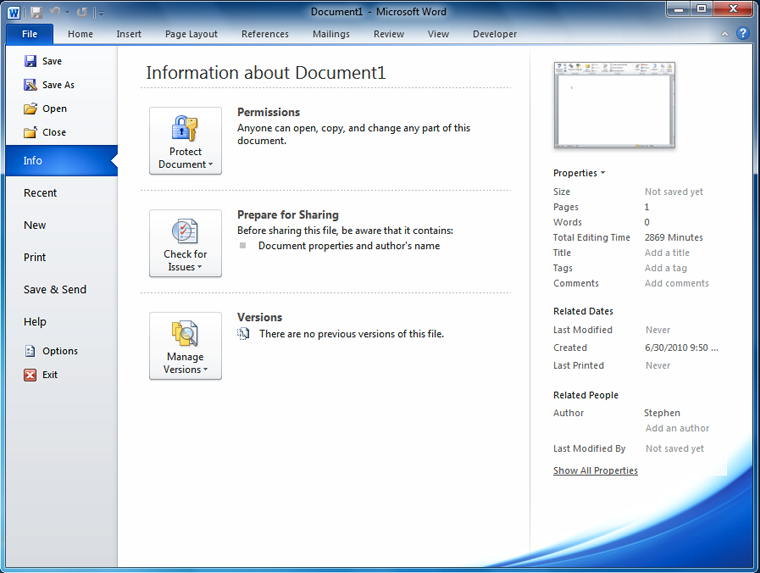
Backstage view
- Backstage view gives you various options for saving, opening, printing, and sharing your files.
- It's similar to the Microsoft Office button menu from Word 2007 and the File menu from earlier versions of Word.
- However, instead of just a menu it's a full-page view, which makes it easier to work with.
III. How To get to Backstage view:
- Click the File tab.
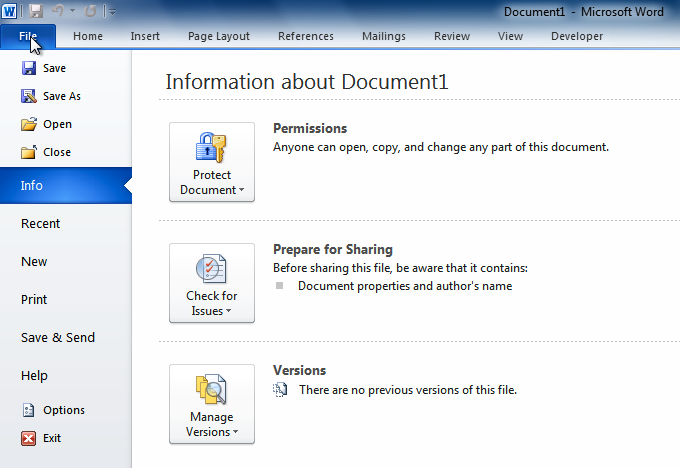
- You can choose an option on the left side of the page.
- To get back to your document, click any tab on the Ribbon.
Click the buttons in the interactive below to learn about the different things you can do in Backstage view.
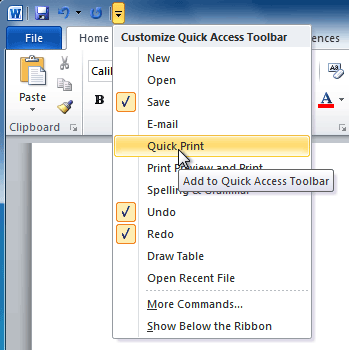
The Quick Access toolbar
- The Quick Access toolbar, located above the Ribbon, lets you access common commands no matter which tab you're on.
- By default, it shows the Save, Undo, and Repeat commands. You can add other commands to make it more convenient for you.
IV. How To add commands to the Quick Access toolbar:
- Click the drop-down arrow to the right of the Quick Access toolbar.
- Select the command you want to add from the drop-down menu. It will appear in the Quick Access toolbar.
The Ruler
- The Ruler is located at the top and to the left of your document.
- It makes it easier to adjust your document with precision.
- If you want, you can hide the Ruler to free up more screen space.
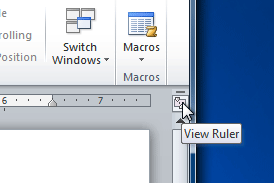
V. How To hide or view the Ruler:
- Click the View Ruler icon over the scrollbar to hide the ruler.
- To show the ruler, click the View Ruler icon again.
Creating and opening documents
- Word files are called documents.
- When you start a new project in Word, you'll need to create a new document, which can either be blank or from a template.
- You'll also need to know how to open an existing document.
VI. How To create a new blank document:
- Click the File tab. This takes you to Backstage view.
- Select New.
- Select Blank document under Available Templates. It will be highlighted by default.
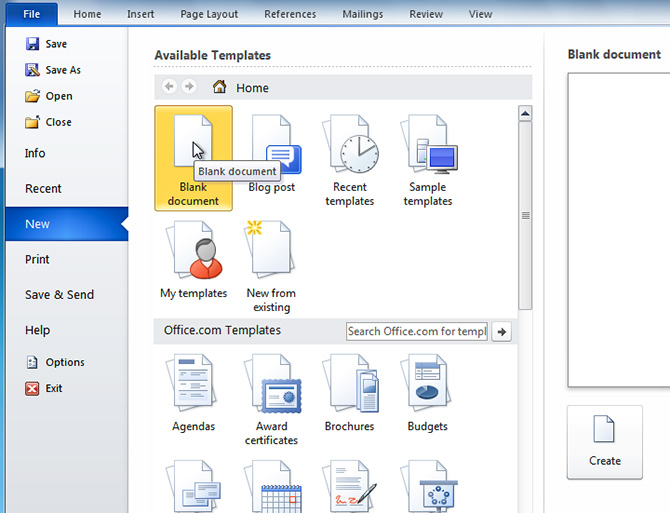
- Click Create. A new blank document appears in the Word window.
To save time, you can create your document from a template, which you can select from the New Document pane. We'll talk about templates in a later lesson.
VII. How To open an existing document:
- Click the File tab. This takes you to Backstage view.
- Select Open. The Open dialog box appears.
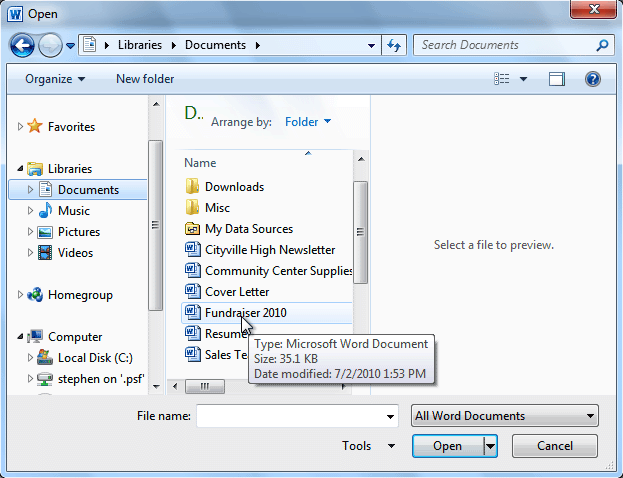
- Select your document, then click Open.
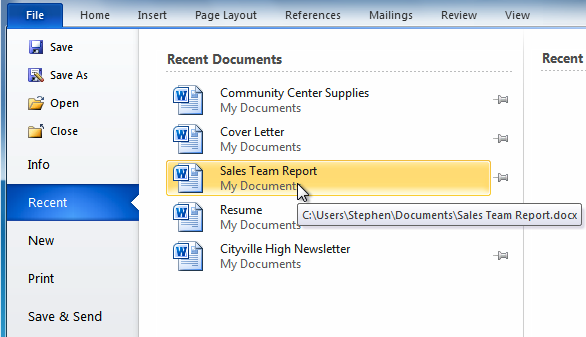
If you've opened a file recently, you can also access it from the Recent Documents list. Just click on the File tab and select Recent.
Compatibility mode
Sometimes you may need to work with documents that were created in earlier versions of Microsoft Word, such as Word 2007 or Word 2003. When you open these types of documents, they will appear in Compatibility mode.
Compatibility mode disables certain features, so you'll only be able to access commands found in the program that was used to create the document. For example, if you open a document created in Word 2007, you can only use tabs and commands found in Word 2007.
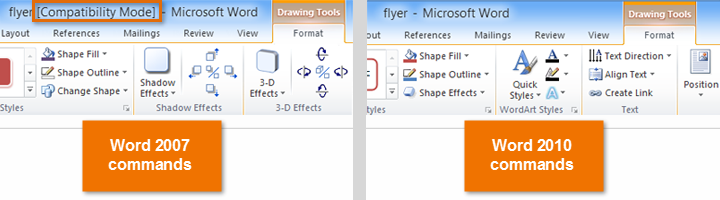
In the image below, you can see how Compatibility mode can affect which commands are available. Because the document on the left is in Compatibility mode, it only shows commands that were available in Word 2007.
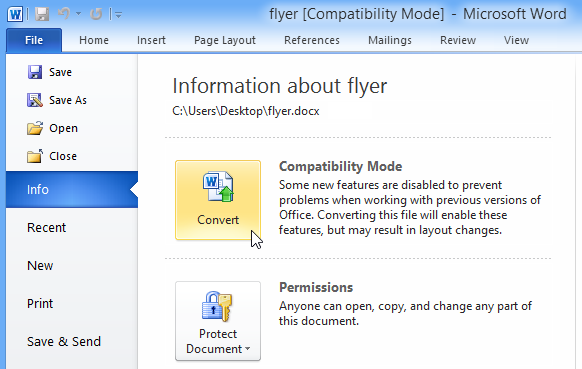
To exit Compatibility mode, you'll need to convert the document to the current version type. However, if you're collaborating with others who only have access to an earlier version of Word, it's best to leave the document in Compatibility mode so the format will not change.
You can review this support page from Microsoft to learn more about which features are disabled in Compatibility mode.
VIII. How To convert a document:
If you want access to all Word 2010 features, you can convert the document to the 2010 file format.
Note that converting a file may cause some changes to the original layout of the document.
- Click the File tab to access Backstage view.
- Locate and select the Convert command.
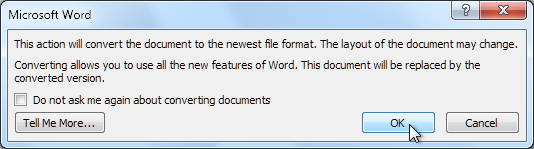
- A dialog box will appear. Click OK to confirm the file upgrade.
- The document will be converted to the newest file type.
Challenge!
- Open Word 2010 on your computer. A new blank document will appear on the screen.
- Make sure the Ribbon is maximized.
- Display the Ruler.
- Add any commands you want to the Quick Access toolbar.
- Close Word without saving the document.
No comments:
Post a Comment