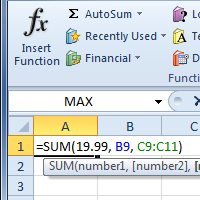
Working with basic functions
In this lesson, you'll learn the basics of inserting common functions into your worksheet by utilizing the AutoSum and Insert Functions commands. You will also become familiar with how to search and find various functions, including exploring Excel's Functions Library.
Basic functions
A function is a predefined formula that performs calculations using specific values in a particular order.
The parts of a function
The basic syntax to create a formula with a function is to insert an equals sign (=), function name (SUM, for example, is the function name for addition), and argument. Arguments contain the information you want the formula to calculate, such as a range of cell references.
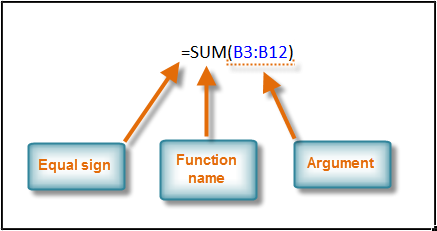
- Colons create a reference to a range of cells.
For example, =AVERAGE(E19:E23) would calculate the average of the cell range E19 through E23.
- Commas separate individual values, cell
references, and cell ranges in parentheses. If there is more than one
argument, you must separate each argument by a comma.
For example, =COUNT(C6:C14,C19:C23,C28) will count all the cells in the three arguments that are included in parentheses.
To create a basic function in Excel:
- Select the cell where the answer will appear (F15, for example).
- Type the equals sign (=), then enter the function name (SUM, for example).
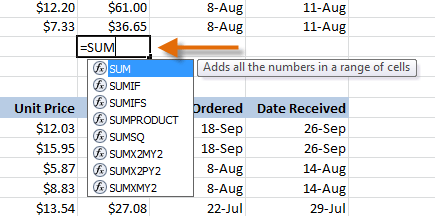
- Enter the cells for the argument inside the parentheses.
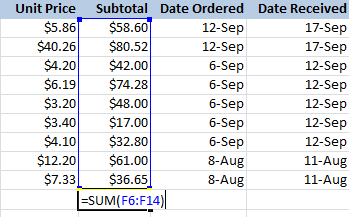
- Press Enter, and the result will appear.
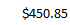
Using AutoSum to select common functions
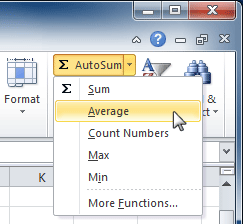
The AutoSum command allows you to automatically return the results for a range of cells for common functions like SUM and AVERAGE.
- Select the cell where the answer will appear (E24, for example).
- Click the Home tab.
- In the Editing group, click the AutoSum drop-down arrow and select the function you want (Average, for example).
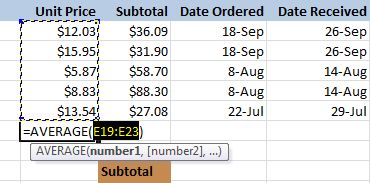
- A formula will appear in E24,
the selected cell. If logically placed, AutoSum will select your cells
for you. Otherwise, you will need to click the cells to choose the
argument you want.
- Press Enter, and the result will appear.
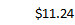
The AutoSum command can also be accessed from the Formulas tab.
Note:- You can also use the Alt+= keyboard shortcut instead of the AutoSum command. To use this shortcut, hold down the Alt key and then press the equals sign.
The Function Library
There are hundreds of functions in Excel, but only some will be useful for the type of data you're working with. There is no need to learn every single function, but you may want to explore some of the different types to get ideas about which ones might be helpful to you as you create new spreadsheets.
A great place to explore functions is in the Function Library on the Formulas tab. Here, you can search and select Excel functions based on categories such as Financial, Logical, Text, and Date & Time. Click the buttons in the interactive below to learn more.
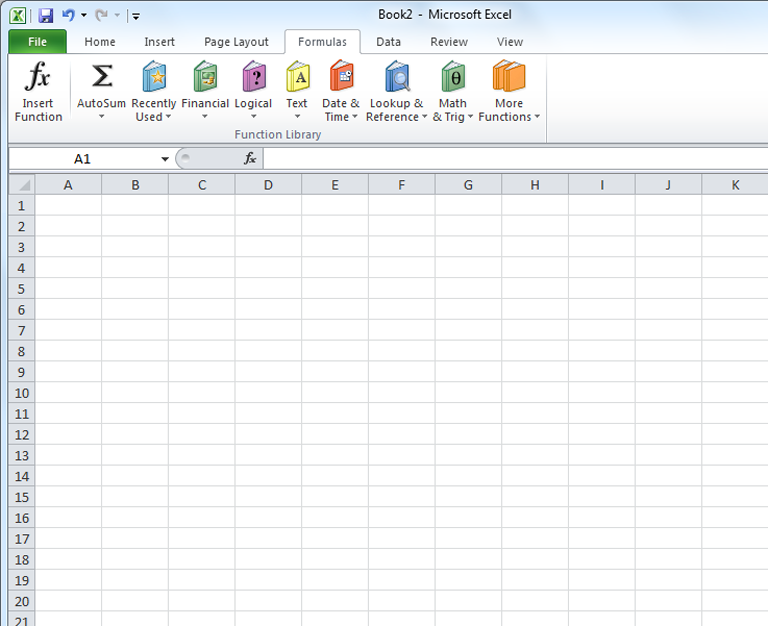
To insert a function from the Function Library:
- Select the cell where the answer will appear (I6, for example).
- Click the Formulas tab.
- From the Function Library group, select the function category you want. In this example, we'll choose Date & Time.
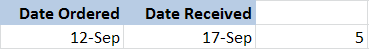
- Select the desired function from the Date & Time drop-down menu. We'll choose the NETWORKDAYS function to count the days between the order date and receive date in our worksheet.
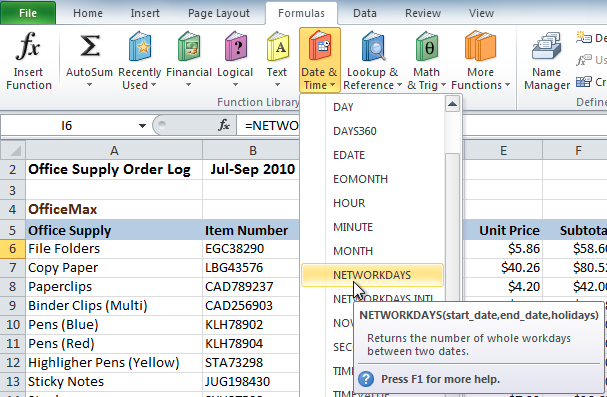
- The Function Arguments dialog box will appear. Insert the cursor in the first field, then enter or select the cell(s) you want (G6, for example).
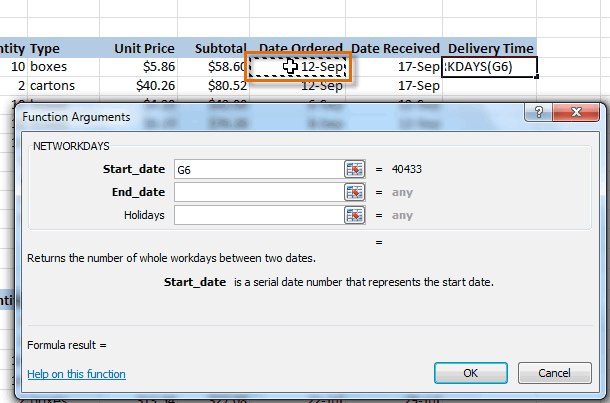
- Insert the cursor in the next field, then enter or select the cell(s) you want (H6, for example).
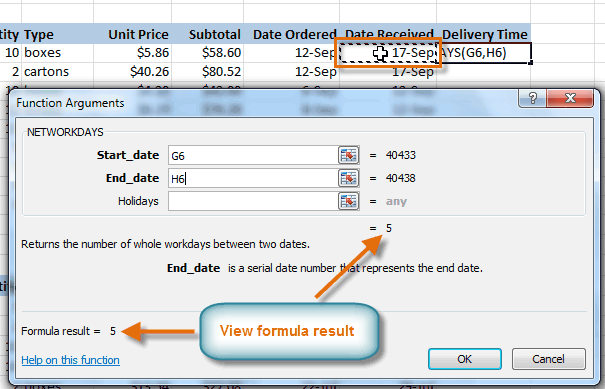
- Click OK, and the result will appear. Our results show that it took five days to receive the order.
Using the Insert Function command
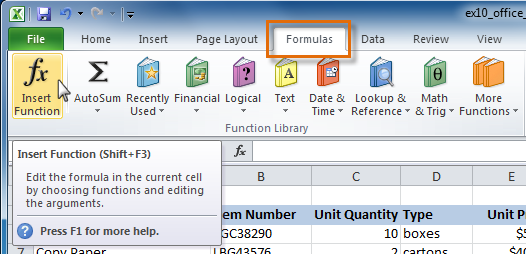
- Select the cell where the answer will appear (A27, for example).
- Click the Formulas tab, then select the Insert Function command.
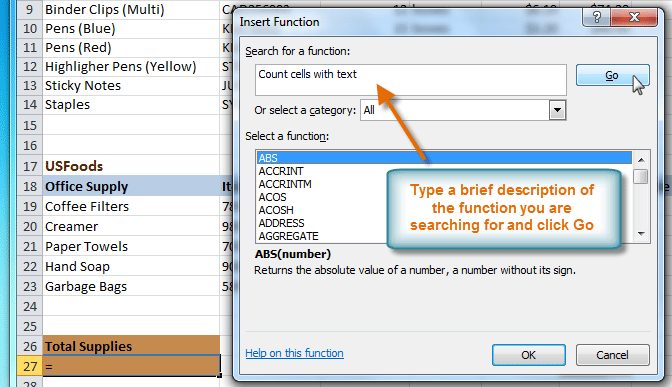
- The Insert Function dialog box will appear.
- Type a description of the function you are searching for, then click Go (Count cells with text, for example). You can also search by selecting a category.
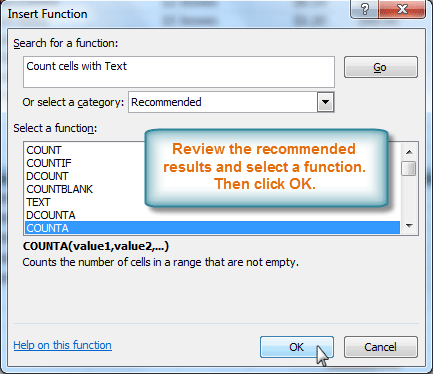
- Review the results to find the function you want (COUNTA, for example). Click OK.
- The Function Arguments dialog box will appear. Insert the cursor in the first field, then enter or select the cell(s) you want (A6:A14, for example).
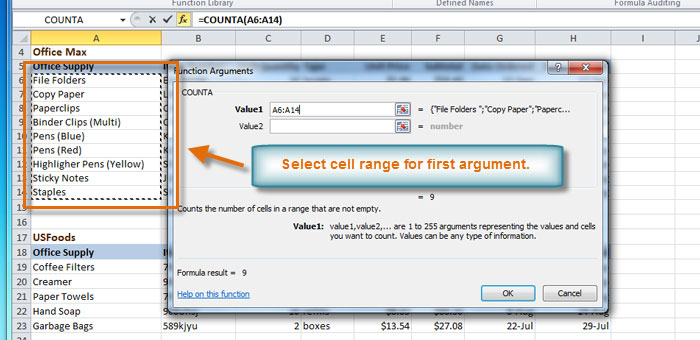
- Insert the cursor in the next field, then enter or select the cell(s) you want (A19:A23, for example). You can continue to add additional arguments if needed.
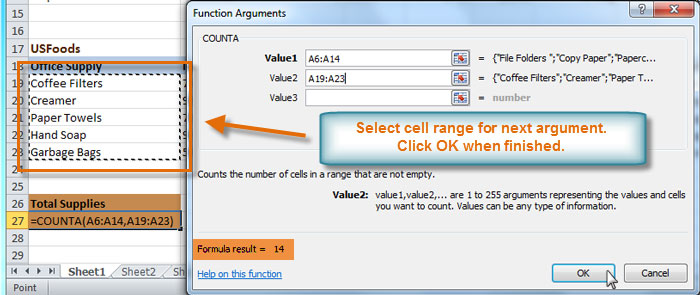
- Click OK, and the result will appear. Our results show that 14 Total Supplies were ordered from our log.

Challenge!
- Open an existing Excel 2010 workbook. If you want, you can use this example.
- Create a function that contains more than one argument.
- Use AutoSum to insert a function. If you are using the example, insert the MAX function in cell E15 to find the highest-priced supply.
- Insert a function from the Functions Library. If you are using the example, find the PRODUCT function (multiply) to calculate the Unit Quantity times the Unit Price in cells F19 through F23.
- Use the Insert Function command to search and explore functions.
No comments:
Post a Comment